
Research
Research
Solid-state LiDAR
Solid-state LiDAR는 기계식 LiDAR와는 달리 모터와 같은 움직이는 파트가 없이 광위상배열 (Optical phased array)를 이용한 위상 변조만으로 빔을 조향할 수 있어 소형화와 대량생산에 유리하며 안정성이 높다. 레이더에 비해 뛰어난 해상도를 가지고 있어 형태 인식에 강점을 가지고 있으며 자율주행 자동차, 로보틱스, 스마트 팩토리 분야에서 활발히 연구되고 있다.
Optical phased array (OPA) devices are being actively investigated to develop compact solid-state beam scanners, which are essential in fields such as LiDAR, free-space optical links, biophotonics, etc. Based on the unique nature of perfluorinated polymers, we propose a polymer waveguide OPA with the advantages of low driving power and high optical throughput. Unlike silicon photonic OPAs, the polymer OPAs enable sustainable phase distribution control during beam scanning, which reduces the burden of beamforming. Moreover, by incorporating a tunable wavelength laser comprising a polymer waveguide Bragg reflector, two-dimensional beam scanning is demonstrated, which facilitates the development of laser-integrated polymeric OPA beam scanners.
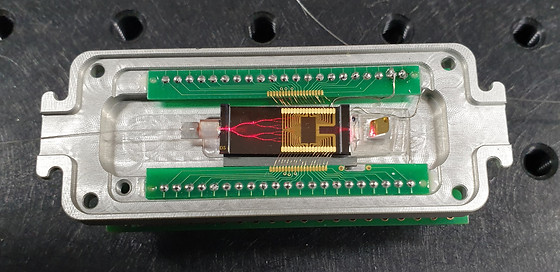
Integrated Optical Current Sensor
광전류센서는 금속 도체 없이 절연체만으로 구성되어 있어 전자기 간섭에 의한 영향을 받지 않으며 넓은 dynamic range를 가지고 있기 때문에 대규모 발전 및 배전 시스템에서 안정적인 전력 모니터링을 수행하는데 있어 효과적이다. 또한 기존 전기식 전류 센서 보다 작고 가볍기에 설치에 용이하고 절연 가스 및 절연유가 필요 없기 때문에 유지 보수 비용이 들지 않는 장점을 가지고 있다.
Various functional optical devices are integrated on a single chip in order to construct optical current transducers based on polarization rotated reflection interferometry, which consists of polarization maintaining 3-dB couplers, TE-pass polarizers, TE/TM polarization converters, and thermo-optic phase modulators. By virtue of the device integration, the sensor exhibited good linearity, and excellent accuracy with an error less than 0.2%. The integrated-optic device provides inherent polarization maintaining characteristics and precise controllability of the optical path length in the interferometric sensor. Single chip integration reduces the complexity of the interferometry, and enables mass-production of low-cost high performance current sensors.

Polymeric Optical Waveguide Devices
폴리머 광도파로 소자는 높은 열광학 효과 (Thermo-optic effect)와 우수한 단열 (heat isolation) 특성으로 인해 작은 전력을 이용하여 안정적인 위상 변조가 가능한 장점이 있다. 따라서 폴리머는 variable optical attenuator, thermo-optic switch, tunable laser, tunable wavelength filter, tunable transceiver, beam scanner 등의 다양한 광학 소자를 제작하는데 핵심적인 소재로써 역할을 한다.
Optical polymers possess in general relatively high thermo-optic coefficients and at the same time low thermal conductivity, both of which make them attractive material candidates for realizing highly efficient thermally tunable devices. Over the years, various thermo-optic components have been demonstrated on polymer platform, covering tunable reflectors and filters as part of a laser cavity, variable optical attenuators (VOAs) as light amplitude regulators in e.g. a coherent receiver, and thermo-optic switches (TOSs) allowing multi-flow control in the photonic integrated circuits (PICs). This work attempts to review the recent progress on the above mentioned three component branches, including linearly and differentially tunable filters, VOAs based on 1×1 multimode interference structure (MMI) and Mach–Zehnder interferometer (MZI), and 1×2 TOS based on waveguide Y-branch, driven by a pair of sidelong placed heater electrodes. These thermo-optic components can well be integrated into larger PICs: the dual-polarization switchable tunable laser and the colorless optical 90° hybrid are presented in the end as examples.
